Zirconia Blocks From the Manufacturer to Your Dental Office
2024-07-13
2024-07-07
Understanding Dental Impression Scanners: How They Work and Their Advantages
In the ever-evolving field of dentistry, technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing patient care and improving clinical outcomes. One such technological advancement is the dental impression scanner. This digital tool is revolutionizing how dentists capture precise images of patients’oral structures, replacing traditional methods that can be cumbersome and uncomfortable. This article delves into the workings of dental impression scanners, their advantages, and their significant impact on modern dentistry.

1. What Are Dental Impression Scanners?
Dental impression scanners are digital devices that capture detailed, 3D images of patients' teeth and gums. Unlike traditional impression methods that use putty-like materials to create molds, digital scanners use advanced imaging technology to produce accurate representations of the oral cavity. These digital impressions are essential for various dental procedures, from crowns and bridges to orthodontic aligners.
Traditional methods often involve multiple steps and can be uncomfortable for patients. In contrast, digital scanners provide a more streamlined and patient-friendly experience, marking a significant advancement in dental technology.
2.How Do Dental Impression Scanners Work?
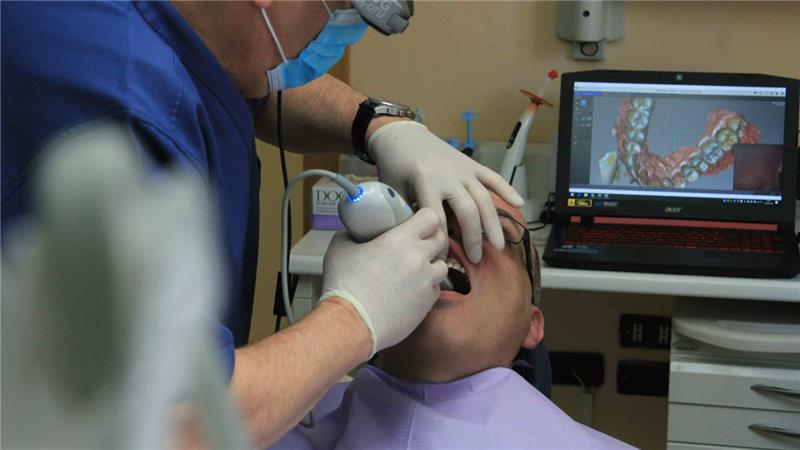
Dental impression scanners are at the forefront of digital dentistry, leveraging advanced imaging technologies to create precise digital models of patients' oral structures. Understanding how these devices work provides insight into their accuracy and efficiency. This section will delve into the types of scanners, their key components, and the step-by-step process involved in capturing a dental impression.
Types of Dental Impression Scanners
Dental impression scanners can be broadly categorized into two types: intraoral scanners and extraoral scanners. Each type has its specific applications and advantages.
Intraoral Scanners:
Usage: Intraoral scanners are handheld devices used directly inside the patient's mouth.
Technology: These scanners utilize light sources such as lasers or structured light to capture detailed images of the teeth and gums.
Portability: Due to their compact and portable design, intraoral scanners are ideal for use in dental clinics for real-time scanning.
Extraoral Scanners:
Usage: Extraoral scanners are stationary devices used to scan dental impressions or models outside the patient's mouth.
Technology: These scanners often employ high-resolution cameras and sophisticated software to digitize physical models with exceptional precision.
Application: Extraoral scanners are commonly used in dental laboratories to create digital records from traditional impressions.
Key Components and Their Functions
Whether intraoral or extraoral, dental impression scanners share several key components that enable their functionality:
Light Source:
The light source, such as a laser or structured light, is crucial for capturing detailed images. It projects light onto the teeth and gums, which reflects back to the scanner's sensors.
Sensors:
The sensors capture the reflected light and convert it into digital data. High-resolution sensors ensure that the captured data is accurate and detailed.
Software:
Advanced software processes the captured data to generate a 3D digital model. This software can correct minor errors, stitch together multiple images, and provide a seamless digital representation of the oral cavity.
Display:
Many intraoral scanners include a display screen where the dentist can view the scanned images in real-time, ensuring accuracy and completeness during the scanning process.
Step-by-Step Process of Taking a Digital Dental Impression
The process of capturing a digital dental impression using an intraoral scanner involves several steps, each contributing to the accuracy and efficiency of the final model.
Preparation:
The dentist begins by preparing the patient's mouth. This involves cleaning and drying the teeth to ensure clear and unobstructed imaging.
Scanning:
The dentist then uses the intraoral scanner to capture images of the teeth and gums. The scanner is moved systematically over the dental arch, capturing detailed images from multiple angles.
Image Capture:
As the scanner moves across the teeth, it projects light and captures the reflected data. The sensors record this information, which is then processed by the scanner's software.
Data Processing:
The captured data is transmitted to the connected software, which processes the images to create a 3D digital model. The software may incorporate algorithms to correct minor distortions and stitch together the images for a cohesive model.
Verification:
The dentist reviews the digital model in real-time on the scanner’s display screen. Any areas that require additional scanning can be identified and rescanned immediately.
Finalization:
Once the scanning is complete, the final digital model is reviewed for accuracy. The model can then be used for various dental applications, such as designing crowns, bridges, or orthodontic aligners.
Benefits of the Digital Process
The digital process of capturing dental impressions offers numerous benefits:
Precision: The high level of detail and accuracy minimizes errors that are common with traditional impression methods.
Speed: The process is quick, often taking only a few minutes, compared to the lengthy setting times of traditional materials.
Comfort: Patients experience significantly less discomfort, as there is no need for messy impression materials.
Real-Time Feedback: Dentists can review the digital model immediately, ensuring completeness and accuracy before concluding the scan.
Dental impression scanners represent a significant technological advancement in dentistry, providing a more efficient, accurate, and comfortable way to capture dental impressions. By understanding how these devices work, dental professionals can better appreciate their value and integrate them effectively into their practice.
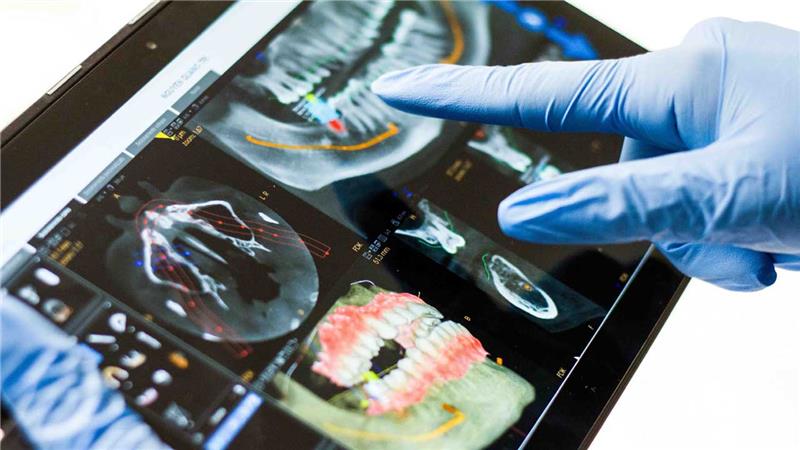
3.Advantages of Using Dental Impression Scanners
The adoption of dental impression scanners has brought about a multitude of benefits that extend to both dental practitioners and patients. This section will explore the various advantages of using digital impression scanners, highlighting how they enhance precision, improve patient comfort, optimize time efficiency, facilitate communication, and reduce the risk of cross-contamination.
Accuracy and Precision
Enhanced Detail and Accuracy:
Dental impression scanners capture highly detailed three-dimensional images of the oral cavity, ensuring that every nuance and contour is accurately represented. Unlike traditional impression materials that can be prone to distortion, digital scanners provide consistent and precise results, minimizing the risk of errors.
Improved Prosthetic Fit:
The superior accuracy of digital impressions leads to better-fitting dental prosthetics, such as crowns, bridges, and dentures. This reduces the need for adjustments and remakes, saving time and resources for both the dentist and the patient.
Consistency and Reliability:
Digital impressions eliminate the variability associated with manual impression-taking techniques. The consistency of digital data ensures reliable outcomes, which is particularly important for complex dental procedures.
Patient Comfort and Experience
Non-Invasive and Comfortable:
Traditional impression methods often involve inserting trays filled with impression material into the patient's mouth, which can be uncomfortable and trigger gag reflexes. In contrast, digital scanners require only a small scanning wand to be moved around the oral cavity, making the process significantly more comfortable for patients.
Reduced Anxiety:
The non-invasive nature of digital scanning can help reduce patient anxiety, particularly for those with dental phobias. The quick and painless procedure contributes to a more positive overall experience.
Shortened Chair Time:
Digital impression-taking is faster than traditional methods, resulting in shorter chair time for patients. This is especially beneficial for busy individuals who appreciate the efficiency of modern dental practices.
Time Efficiency for Dental Clinics
Streamlined Workflow:
The digital impression process is streamlined and efficient, reducing the time required for capturing and processing impressions. This allows dental professionals to see more patients and perform more procedures in a given timeframe.
Immediate Data Availability:
Digital impressions are available for review and use immediately after scanning. This eliminates the need for time-consuming steps such as setting, hardening, and shipping traditional impressions to dental labs.
Quicker Turnaround Times:
The efficiency of digital impressions leads to faster turnaround times for dental restorations and appliances. Dental labs can begin working on the digital models immediately, reducing the overall treatment time for patients.
Enhanced Communication with Dental Labs
Seamless Data Transfer:
Digital impressions can be easily shared with dental labs via secure electronic means. This facilitates seamless communication and collaboration between the dental clinic and the lab, ensuring that the lab technicians have all the necessary data to create precise restorations.
Remote Consultations:
Dentists can consult with lab technicians remotely, discussing the digital models and making adjustments in real-time. This level of collaboration enhances the quality of the final product and reduces the likelihood of errors.
Traceability and Documentation:
Digital impressions provide a clear and traceable record of the patient's oral structures. This documentation can be stored electronically, making it easy to reference for future treatments and ensuring continuity of care.
Reduced Risk of Cross-Contamination
Hygienic Process:
Digital impression scanners eliminate the need for physical impression materials, which can harbor bacteria and pose a risk of cross-contamination. The scanning process is clean and hygienic, promoting a safer environment for both patients and dental staff.
Disposable Sleeves:
Many intraoral scanners come with disposable sleeves that cover the scanning wand. These sleeves can be easily replaced between patients, further reducing the risk of cross-contamination and ensuring compliance with infection control protocols.
Minimized Handling:
The digital workflow minimizes the handling of physical impressions, reducing the potential for contamination at various stages of the process. This enhances the overall safety and hygiene of dental procedures.
4.Common Applications of Dental Impression Scanners
Dental impression scanners are versatile tools used in various fields of dentistry:
Orthodontics: For designing braces and aligners.
Prosthodontics: For creating crowns, bridges, and dentures.
Implantology: For planning and placing dental implants.
Cosmetic Dentistry: For designing veneers and other aesthetic treatments.
5.Challenges and Considerations
While the advantages are clear, there are some challenges to consider:
Initial Investment: The cost of acquiring dental impression scanners can be high.
Learning Curve: Dental professionals may require training to effectively use these devices.
Software Compatibility: Ensuring the scanner software integrates seamlessly with existing systems can be a concern.