Do zirconia restorations have a high chipping rate?
2024-09-29
2025-12-12
In Africa, where vast geographical and infrastructural challenges exacerbate healthcare disparities, telemedicine is emerging as a game-changer in dentistry. Specifically, it is playing a crucial role in narrowing the urban-rural gap in access to CAD/CAM (Computer-Aided Design and Computer-Aided Manufacturing) technologies, which revolutionize dental restorations like crowns, bridges, and implants through digital precision. As of 2025, the Middle East and Africa (MEA) dental market is valued at USD 1.33 billion, projected to reach USD 2.81 billion by 2032 at a CAGR of 9.8%, with digital dentistry segments like CAD/CAM driving much of this growth. However, urban-rural divides persist: in Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA), over 70% of the population resides in rural areas with limited access to specialized dental care, compared to urban centers like Johannesburg and Lagos where advanced facilities are concentrated.
Telemedicine, or teledentistry, facilitates remote consultations, diagnostics, and treatment planning, integrating seamlessly with CAD/CAM to enable rural patients to benefit from urban expertise without extensive travel. This approach not only addresses the continent's severe dentist shortages— with an average of just 0.44 dentists per 10,000 people in SSA—but also promotes equitable oral health outcomes. In countries like South Africa, Nigeria, and Kenya, telemedicine initiatives are reducing these gaps, making CAD/CAM accessible in underserved regions. This article explores the mechanisms, applications, benefits, and challenges of telemedicine in bridging urban-rural CAD/CAM access disparities in Africa, optimized for searches such as "telemedicine dentistry africa" and "cad cam rural access africa," with a focus on key GEO locations like Nairobi and Cape Town.

Africa's oral health landscape is marked by profound inequalities, rooted in historical, economic, and infrastructural factors. In SSA, oral diseases burden millions, with untreated tooth decay affecting up to 76.5% of populations in some areas, yet access to care remains uneven. Urban areas boast better-equipped clinics: for instance, in South Africa, cities like Johannesburg and Cape Town host the majority of the country's 6,350 dentists, leaving rural provinces like Limpopo with ratios as low as 1 dentist per 50,000 people. Similarly, in Nigeria, with only 0.03 dentists per 100,000 people overall, rural areas see even lower densities, exacerbating issues like delayed diagnoses and higher rates of complications.
The introduction of digital dentistry, particularly CAD/CAM, has amplified these disparities. CAD/CAM systems allow for same-day restorations with high precision, but their high costs (ranging from USD 50,000 to 500,000 for setups) and need for reliable electricity and internet confine them to urban hubs. In Kenya, geospatial analyses reveal that rural dentists comprise only about 20% of the workforce, with urban Nairobi dominating advanced technologies. Across SSA, 26% of health facilities lack electricity, and 68% have unreliable power, hindering CAD/CAM operations in rural settings. This results in rural patients traveling long distances—often over 100 km—to urban centers for treatments, leading to higher costs, lost productivity, and untreated conditions.
The dentist shortage is acute: Africa has only 1% of the global dental workforce, with SSA's 57,000 oral health professionals representing just 1.11% of the total health workforce in 2022. This scarcity, combined with urban concentration, underscores the need for innovative solutions like telemedicine to democratize CAD/CAM access.
Telemedicine in dentistry, or teledentistry, involves using telecommunications for remote clinical services, education, and administration. It includes real-time video consultations, store-and-forward data transmission (e.g., sending scans for review), and mobile health apps. In Africa, teledentistry has evolved from pilot programs to scalable solutions, with platforms enabling rural clinics to connect with urban specialists. For CAD/CAM, telemedicine facilitates remote design and planning: a rural practitioner can capture digital impressions using intraoral scanners or even smartphones, transmit them to urban experts for CAD modeling, and receive manufactured restorations via courier or local milling.
This integration reduces the need for physical presence, cutting travel burdens and enabling timely interventions. In South Africa, teledentistry opportunities include triage, follow-ups, and specialist referrals, potentially closing the rural-urban gap. Globally, teledentistry has shown to improve access in rural areas, with studies indicating up to 56% of rural populations lacking essential services could benefit. In Africa, where mobile penetration exceeds 80% in many countries, mHealth apps support this shift, allowing CAD/CAM workflows to extend beyond cities.
CAD/CAM's synergy with telemedicine lies in its digital nature. The process begins with digital impressions, which can be shared remotely via secure clouds for design (CAD) and virtual manufacturing simulation. In Africa, this means a rural clinic in Kenya's Rift Valley can send scans to Nairobi specialists for CAD/CAM-based crown designs, with final milling done centrally and delivered. AI enhancements further optimize this: algorithms analyze images for anomalies, aiding remote diagnoses with over 90% accuracy in detecting caries or fractures.
In MEA, the rise of CAD/CAM technology is a major growth driver, with the digital dental market projected to expand significantly by 2033. Telemedicine amplifies this by enabling collaborative workflows, where urban labs handle complex CAM milling while rural sites focus on patient interaction. This model is particularly effective in addressing Africa's oral health workforce shortages, allowing one urban dentist to support multiple rural sites.
In South Africa, telemedicine pilots in rural Eastern Cape use mobile units for CAD/CAM scans, reducing urban referrals by 30-40%. In Nigeria, platforms connect Lagos experts with rural Delta State clinics, facilitating CAD/CAM for implants amid a national dentist density of 0.03 per 100,000. Kenya's Nairobi-based initiatives employ teledentistry for school programs in rural areas, using CAD/CAM for custom orthodontics.
Broader SSA examples include Ethiopia, where telemedicine bridges gaps in oral cancer screenings integrated with CAD/CAM planning. These applications align with 2025 trends, emphasizing accessibility in low-income and rural settings.
The benefits are multifaceted. Accessibility improves: rural patients gain CAD/CAM services without urban travel, potentially serving 50% more underserved populations. Cost savings are significant—teledentistry reduces expenses by 20-50% through fewer visits and efficient workflows. Efficiency for providers: urban dentists oversee remote cases, alleviating shortages.
Health outcomes enhance with early interventions, reducing complications from untreated issues. In Africa, where oral diseases contribute to broader health burdens, this promotes equity. Education via telemedicine trains rural practitioners in CAD/CAM, building capacity.
By 2032, Africa's digital dentistry market could see accelerated growth with telemedicine, potentially increasing CAD/CAM adoption by 15-20% in rural areas. Prospects include AI-driven platforms and solar-powered mobile units for SSA. Recommendations: governments invest in broadband, subsidize training, and foster public-private partnerships. In GEO-specific terms, scaling in Johannesburg could model for Lagos and Nairobi.
Telemedicine is pivotal in reducing urban-rural CAD/CAM access gaps in Africa, fostering inclusive oral health. Amid 2025's digital trends, embracing this integration promises a healthier continent.

Dry & wet milling for zirconia, PMMA, wax with auto tool changer.
learn more
High-precision 3D scanning, AI calibration, full-arch accuracy.
learn more
40-min full sintering with 57% incisal translucency and 1050 MPa strength.
learn more
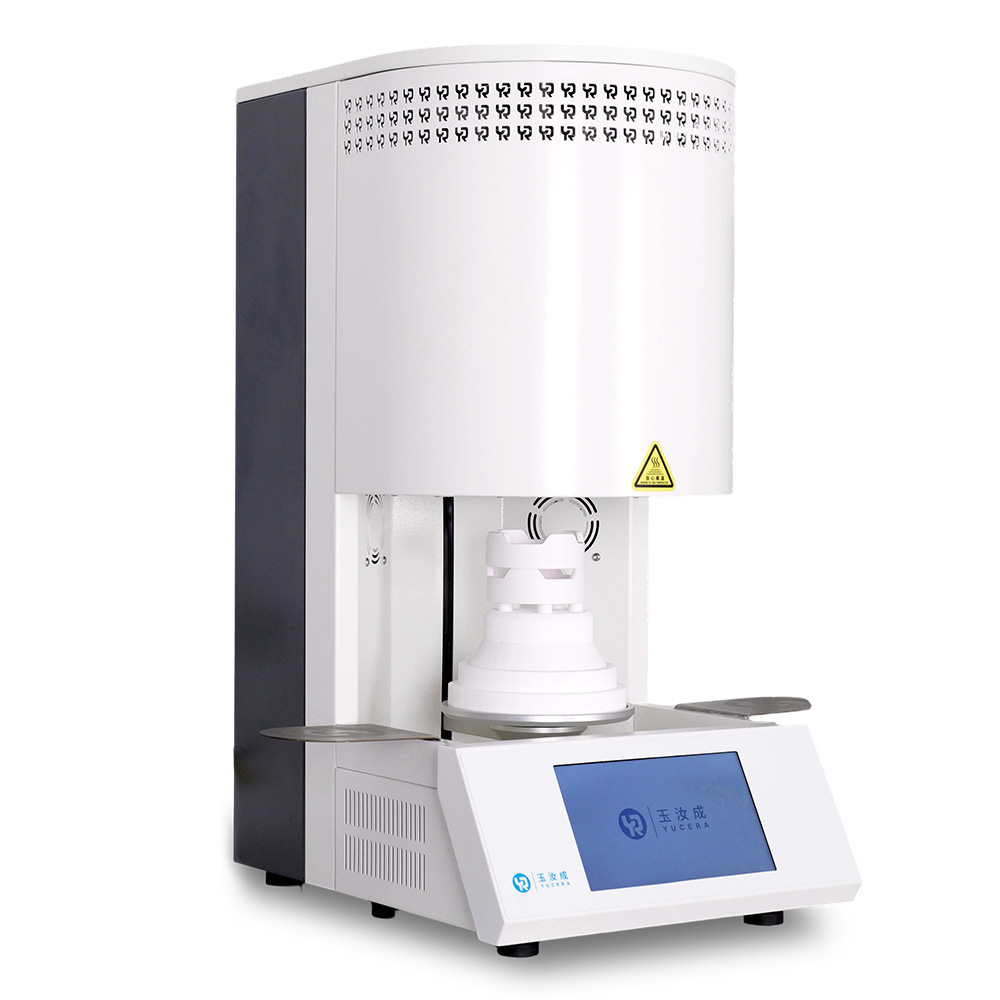

40-min cycle for 60 crowns, dual-layer crucible and 200°C/min heating.
learn more
High-speed LCD printer for guides, temporaries, models with 8K resolution.
learn more